SSC’s approach to the challenge of Food and Nutritional Security (FNS)
The prevalence of hunger and poverty in the Latin-American and Caribbean (LAC) region is a priority challenge on the regional development agenda.

According to the 2023 Regional Overview of Food Security and Nutrition, between 2021 and 2022, the number of people affected by hunger in the region is estimated to have fluctuated between 38.5 million and 51 million. Considering the mid-range of this estimate, 43.2 million people suffered from hunger in 2022 (FAO et al., 2023, p. 2).
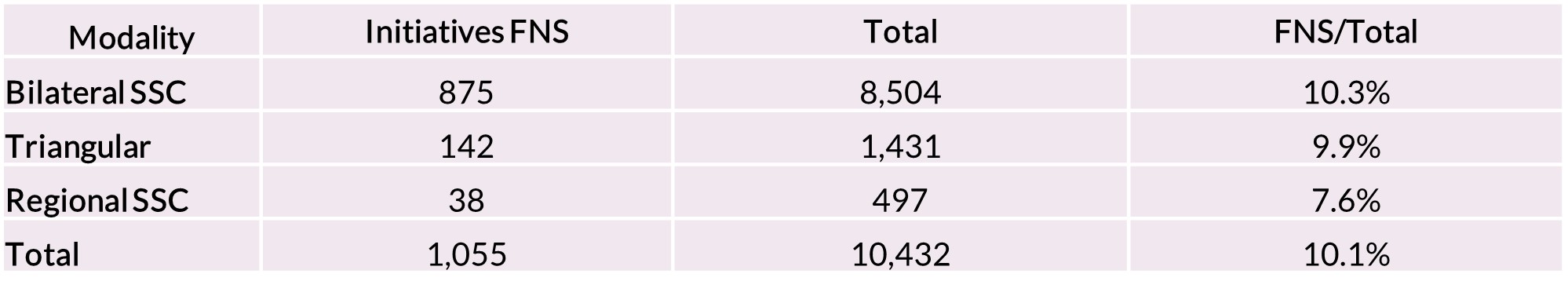
Intense efforts are being made, at the national and local levels, to address this challenge, and international cooperation —particularly South-South and Triangular Cooperation— can be an effective instrument to tackle it. As shown in the following chart, between 2007 and 2023, Ibero-American countries have implemented 1,055 initiatives that focused on FNS, corresponding to 10% of the region’s total cooperation. By modality, cooperation on FNS accounted for around 10% of Bilateral and Triangular exchanges, and represented 7.6% of Regional SSC initiatives.
Initiatives on Food and Nutritional Security (FNS) and total number of initiatives, by cooperation modality. 2007-2023.
In units and percentage.
Source: SEGIB based on Agencies and Directorates-General for Cooperation.
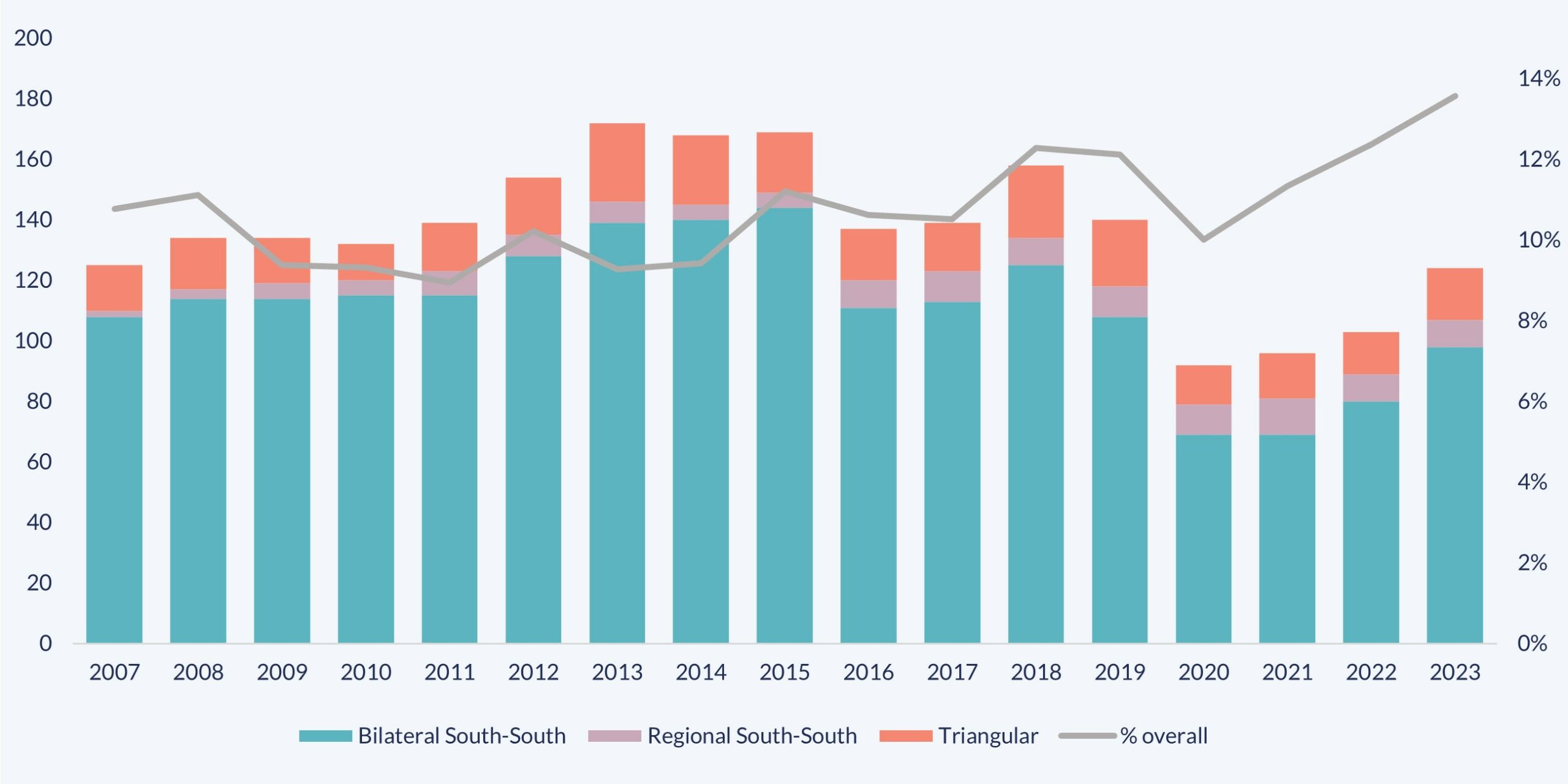
According to the graph, between 2007 and 2015, it is possible to identify a 36% growth in initiatives on FNS (from 125 to 170), which is followed by two significant drops, one in 2016 and others in 2020, coinciding with the impact of the COVID-19 crisis. However, after this last decline, cooperation on FNS recovers, with a positive increase of 29% in the 2021-2023 period, a percentage which is higher than that corresponding to all cooperation (8%). As a result, the importance of FNS as a percentage of the total number of initiatives has increased over the last three years to 14%, a figure 4 percentage points above the average of previous years.
Evolution of the initiatives on FNS, by cooperation modality and percentage in the total number of initiatives. 2007-2023.
In units and percentage.
Source: SEGIB based on Agencies and Directorates-General for Cooperation.
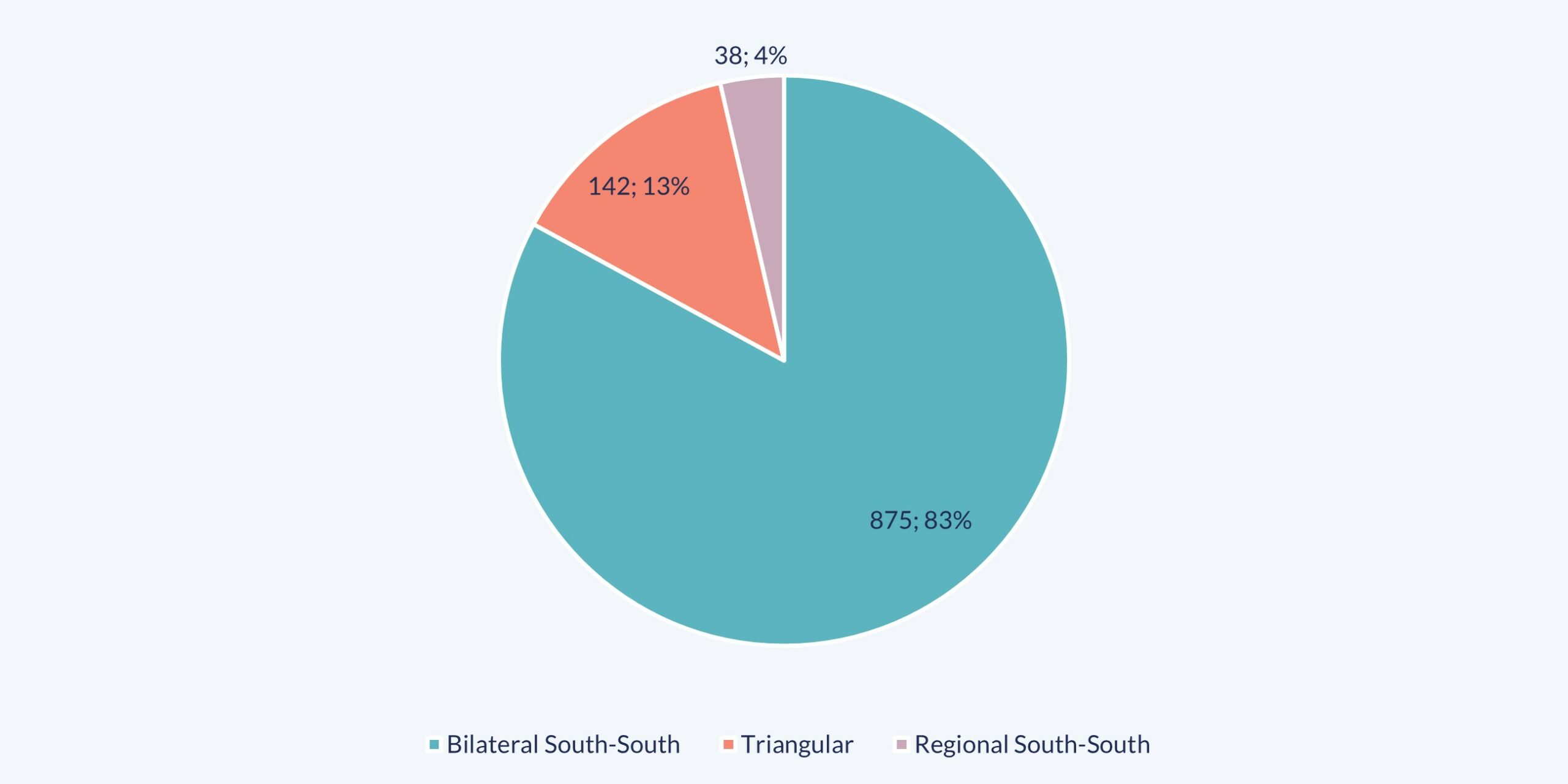
The second graph, in turn, illustrates the distribution of the total number of initiatives on FNS by cooperation modality, in the 2007-2023 period. It suggests that, of the 1,055 initiatives that served this purpose, 83% were implemented through Bilateral SSC, 13% through Triangular Cooperation and 4% through Regional SSC.
Distribution of the initiatives on FNS, by cooperation modality. 2007-2023.
In units and percentage.
Source: SEGIB based on Agencies and Directorates-General for Cooperation.
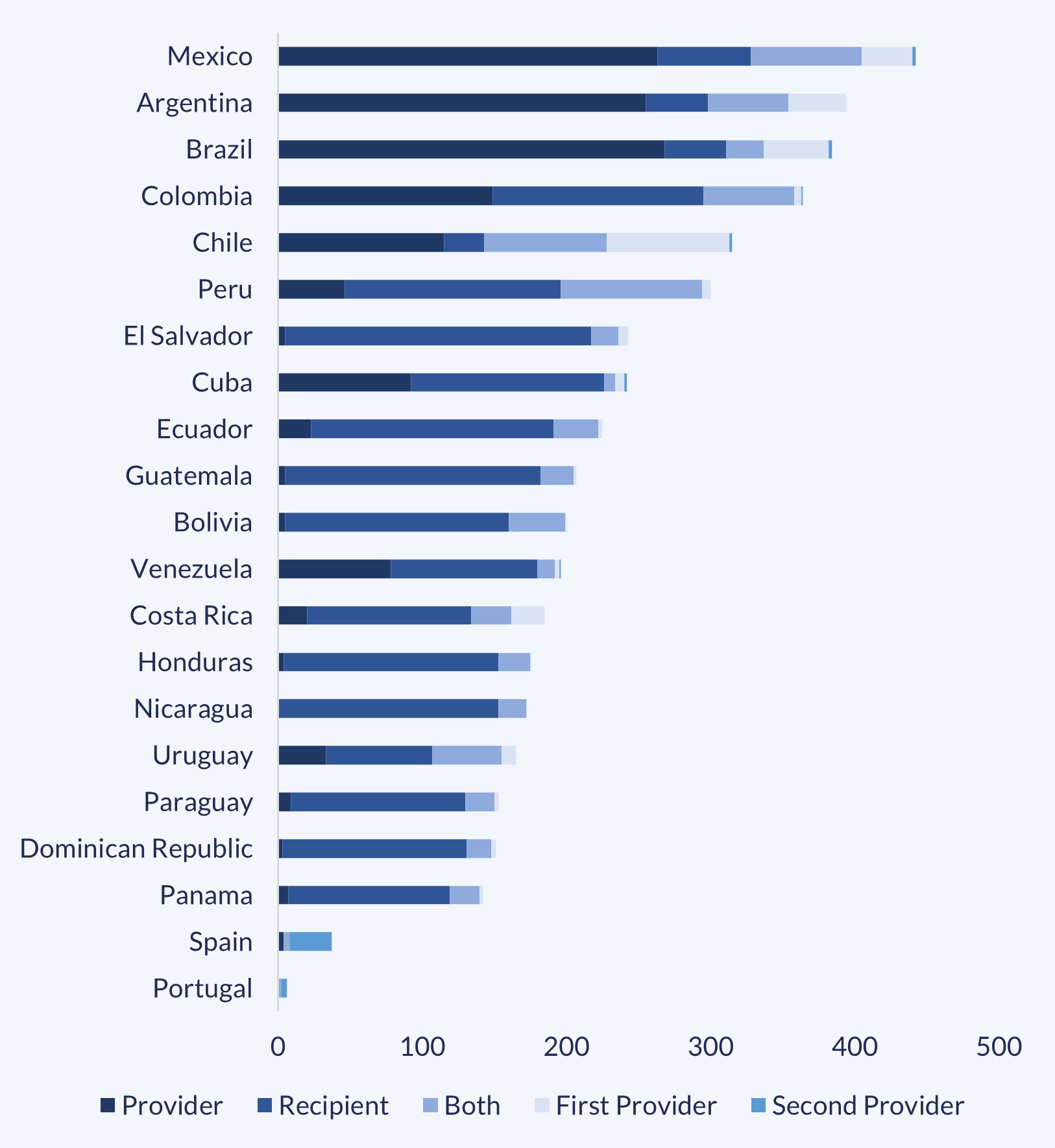
On the other hand, a third graph was prepared to identify the Ibero-American countries that most actively participated in this cooperation. This graph shows the number of initiatives that, between 2007 and 2023, were dedicated to this topic, by country and by the different roles.
Ibero-American countries’ initiatives on FNS, by role. 2007-2023.
In units.
Source: SEGIB based on Agencies and Directorates-General for Cooperation.
It is possible to identify three groups of countries: first, Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Chile and Peru, all with more than 300 exchanges; second, El Salvador, Cuba, Ecuador, Guatemala, Bolivia, Venezuela, Costa Rica, Honduras, Nicaragua, Uruguay, Paraguay, the Dominican Republic and Panama, with between 100 and 300 exchanges; and third, Spain and Portugal, with less than 100 exchanges.
The majority of the most dynamic countries participated as providers in this cooperation, Colombia and Peru being the only exceptions. The former predominantly had a dual role, combining its participation as provider and recipient, while the latter mainly stood out as recipient.
In order to explain how Ibero-American SSC has responded to this challenge, the following graph distributes the 506 initiatives that between 2015 and 2023 addressed FNS, according to their thematic priorities. Eighty-eight percent of the exchanges (445) focused on strengthening Production, and those dedicated to Distribution (25, corresponding to 5%), Consumption (22, accounting for 4.3%) and FNS in general (14, representing 2.7%) were more specific. These 445 initiatives aimed to support the Agriculture and livestock (72%) sector and, to a less extent, Food industry (12.4%); Aquaculture and fisheries (12.2%); and Beekeeping (3.4%).
Distribution of the initiatives on FNS, by category and subcategory. 2015-2023.
In units.
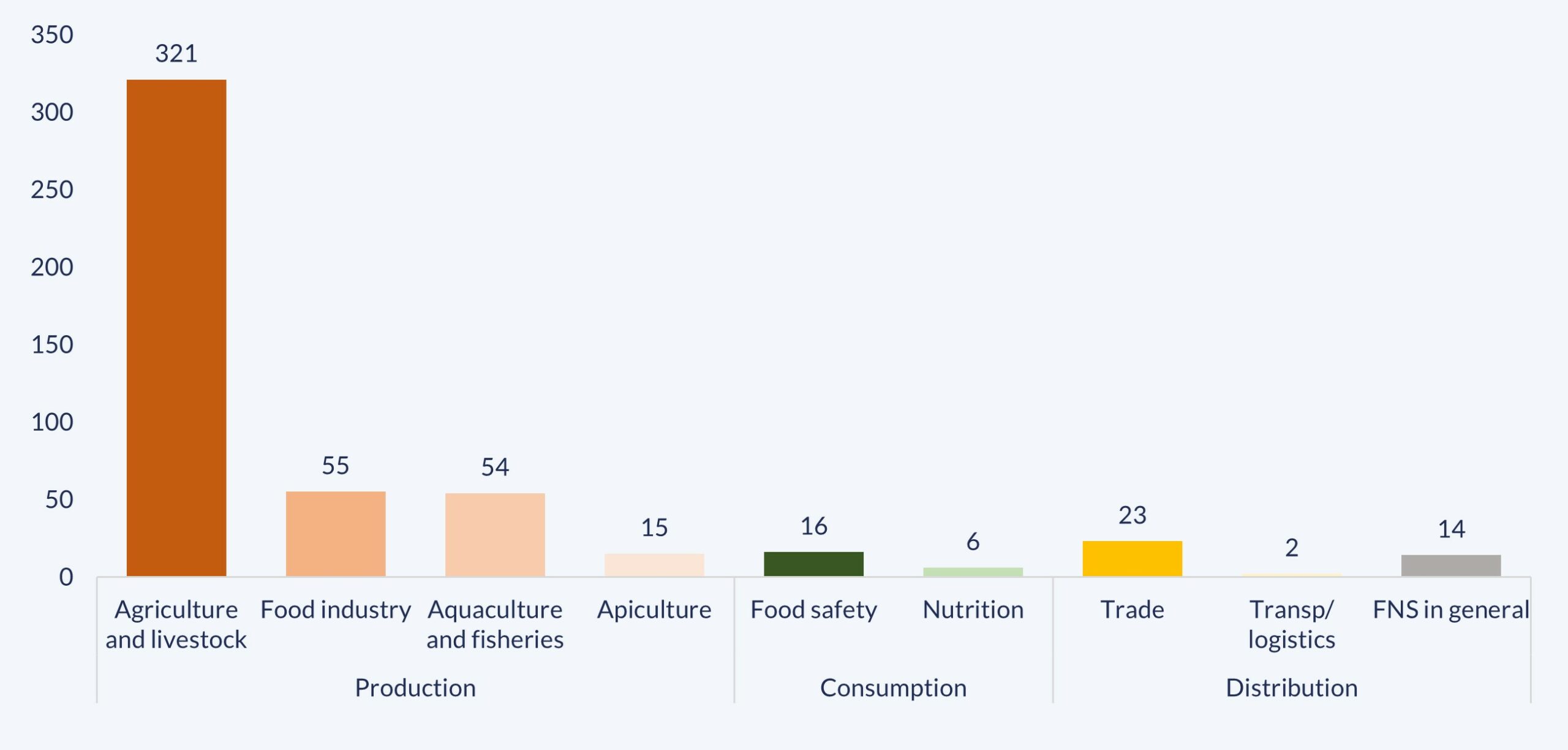
In terms of Production, and in the Agriculture and livestock category, the initiatives that supported family and subsistence agriculture to improve their productivity, competitiveness and the capacities of small-scale producers stood out. Projects that addressed the recovery of degraded soils; the efficient use of water for agricultural production; and irrigation techniques, were also frequent. Additionally, the exchanges on animal and plant health and those related the genetic improvement of agricultural products and livestock to increase productivity and resistance to adverse weather conditions —which are becoming increasingly frequent as a result of climate change—, also deserve a special reference.
On the other hand, initiatives associated with the Food industry subcategory mainly focused on agrifood production chains and productive and territorial development models; on strengthening agroforestry and vegetable systems; on generating capacities, technologies and best practices in agroindustry; and on promoting the association of agricultural producers in cooperatives.
In turn, initiatives on Aquaculture and fisheries reinforced capacities in regulations and fisheries management models (prevention of illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing); sustainable livestock production; the promotion of fisheries and aquaculture’s circular economy.

Between 2015 and 2023, the second most recurrent category was Distribution. These initiatives were mainly dedicated to Trade (92%) and Transportation and logistics (8%). In general, the exchanges focused on strengthening rural cash registers; developing traceability systems for agricultural, aquaculture and fishery goods; modernizing bovine certification processes; assessing risks in import processes; and applying alternative technologies for post-harvest grain storage, to mention a few examples.
Initiatives aimed at strengthening Consumption followed, distributed in topics related to Safety (73%) and Nutrition (27%). The former addressed the different aspects which are necessary to ensure that food and water are safe for human consumption, specifically through the strengthening of regulatory frameworks for activities with Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs); the generation of capacities in official inspection systems and quality management to guarantee safety; and the management and handling of pesticide and micro-plastic residues. In terms of Nutrition, the main topics included breastfeeding; nutritious food in childhood; obesity prevention; and food labeling, among others.
Finally, the 14 initiatives that were classified in the FNS in general category heterogeneously tackled various aspects for a comprehensive strategy on the sector, including hunger reduction and rural development.
May 2024
***
Source: SEGIB based on Agencies and Directorates-General for Cooperation and FAO et al. (2023).
Photos: Image bank on South-South and Triangular Cooperation in Ibero-America. SEGIB-PIFCSS. 2021-2024.

